What Hybridization Best Describes the Bond
Two such regions imply sp hybridization. During hybridization C-C sigma bond is formed when one sp orbital overlaps from each of the carbons and two C-H bonds are created when second sp orbital on each carbon overlaps with 1s orbital of hydrogen.
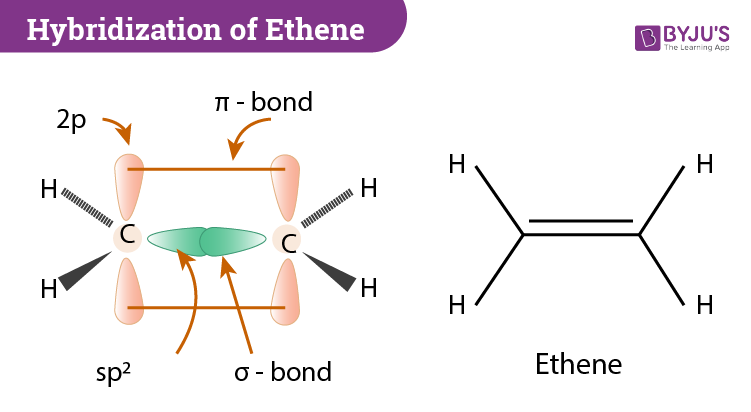
Hybridization Of C2h4 Ethene Hybridization Of Carbon In C2h4
The sigma bond between the two carbon atoms is formed between two.
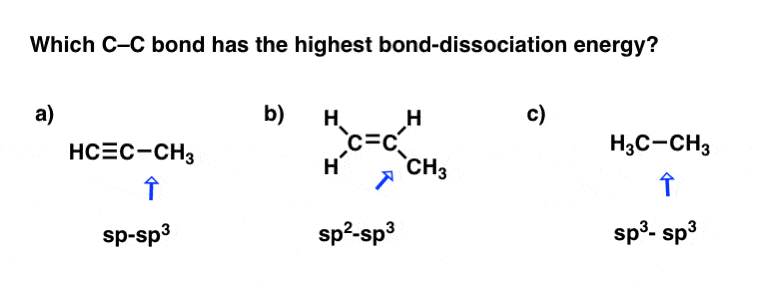
. Based on valence bond theory what is the hybridization of. There is a π-bond formed between a non-hybridized C p-orbital overlapping with an O p-orbital. Question 2 1 point Based on valence bond theory which statement best describes the electron geometry and hybridization of the central atom s in acetylene.
The electron geometry of carbon in a carbonate anion is trigonal planar with a sp2 hybridization and bond angles are 120. Ok now when we know that hybridization is a model and not an actual process lets look at how this process happens. The electron geometry of the 2 carbons in acetylene is trigonal planar with a sp 2 hybridization.
Hybridization of bonds takes place when you have overlap of two different orbitals. In order to overlap the orbitals must match each other in energy. Formation of the Hybridized Orbitals.
There are 3 types of hybridizations. Hybridization and hybrid orbitals. Pi π Bonds form when two un-hybridized p-orbitals overlap.
The electron geometry of the 2 carbons in acetylene is tetrahedral. The hybrid orbitals scattered in space and tend to the farthest apart. Which statement best describe the structure of carbonate anion.
Pi π bonds are formed from unhybridized atomic orbitals p or d orbitals. Hybridization is a mathematical model that describes how the atomic orbitals wouldve looked like based on the observable molecular orbitals. A Covalent bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one element to.
If we look at the carbon atom. Why the bonds of methane are the same that otherwise do not make sense. The three hybrids will be used to make.
Hybridized orbitals are very useful in explaining of the shape of molecular orbitals for molecules and are an integral part of valence bond theory. We can determine the type of hybridization around a central atom from the geometry of the regions of electron density about it. Four sp 3 hybridization.
In this the carbon atom will have two half-filled 2p orbitals. In general you need to use each time the theory that best describes the result. This theory is especially useful to explain the covalent bonds in organic molecules.
Each bond takes 2 electrons to complete. Which statement best describes the orbital hybridization used to form bonds in the cation below. The numbers of atomic orbitals mixed together are always equal to the number of hybrid orbitals.
Up to 10 cash back Possible Answers. The sigma bond between the C and N is formed between an sp2 hybridized C anti an The sigma bond between the two carbons is formed between one sp2 hybridized C. B Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
As it has already been said hybridisation is a theory we use so as to explain things eg. Based on valence bond theory which statement best describes the electron geometry and hybridization of the central atom in acetylene H2CCh2. Other times youll use the valence bond theory or other times youll use the molecular orbitals theory.
And six sp 3 d 2 hybridization. In chemistry hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for describing bonding properties. C Ionic bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two nonmetals.
The steric number gives you the geometry of the molecule. Pi π Bond. One p-orbital is needed to make the double-bond to the other carbon.
With carbon it is s and p orbitals. During hybridisation the mixing of a number of orbitals is as per requirement. Remember that π bonds unlike sigma bonds are made from p-orbitals.
The octahedral shape looks like two pyramids with four sides each that have been stuck together by their bases. Now when the hybridization happen there is one less available p-orbtial and so a total of 1 s orbital and 2 p-orbitals are mixed together to make three sp 2 orbitals. Which choice best describes the polarity of IF5.
Hybrid bonds are stronger than the non-hybridised bonds. D Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two metals. Three sp 2 hybridization.
The platinum molecule is able to bind six fluorine molecules due to the availability of d orbitals in its valence shell. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Determine the type or types of hybridization that could lead to hybrid orbitals at the specified angle.
Five sp 3 d hybridization. Finding the hybridization of atoms in organic molecules. The sum of the number of covalent bonds and the number of lone pairs of electrons on the central atom gives the steric number.
The only answer choice that works is platinum hexafluoride. The C-Cl bond is a std. The electron geometry of the 2 carbons in acetylene is linear with the sp hybridization.
Mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals suitable for pairing electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory Boron trifluoride BF 3 has a boron atom with three outer-shell electrons in its normal or ground state as well as three fluorine atoms each with seven outer electrons. The process by which all of the bonding orbitals become the same in energy and bond length is called hybridization. This is what I call a side-by-side bond.
Hybridization is a concept used in organic chemistry to explain the chemical bonding in cases where the valence bond theory does not provide satisfactory clarification. This is the currently selected item.

On Hybrid Orbitals And Bond Strengths Master Organic Chemistry
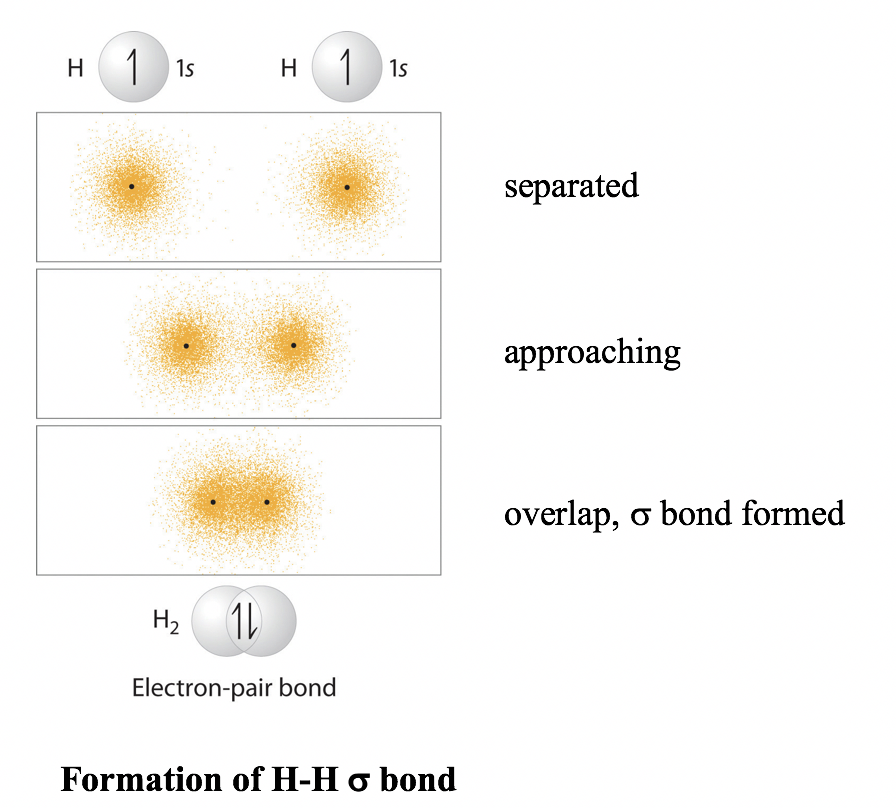
1 6 Valence Bond Theory And Hybridization Organic Chemistry I

No comments for "What Hybridization Best Describes the Bond"
Post a Comment